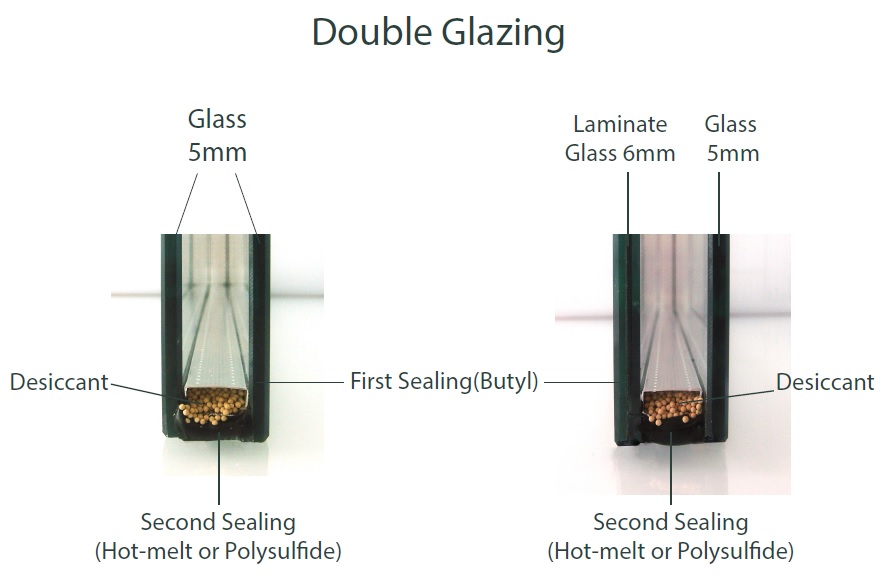
Dear customers/cooperators,
Choosing the double glazing for your house is extremely important, since it contributes to the thermal losses with a percentage of 20-30%, especially during sunlight period of the year. However, regardless the fact that with technology, the performance of the glass is constantly strengthened and thus helping in the long-term saving of a household, in majority the owner, having first in mind the budget will choose the cheapest solution of today.
The purpose of what follows, is to present to you simple but in the same time very important details for the double glazing and the options you have, which are vital for you to know before you take your final decision. Double Glazing usually refers to two panes of glass enclosing a hermetically closed air space. Variation in the thickness of the two glasses, their type, the thickness of the gap (the alouminium spacer between them) and also what the gap is filled with (air or argon), affects factors such as the degree of thermal insulation, sound insulation and safety provided by the double glazing.
To make the right choice, you need to know at the same time some details for solar energy. The sun releases energy, which reaches the earth in the form of radiation (solar spectrum) and which is separated as you will see in the picture below into: ultraviolet radiation (UV), visible radiation (visible light), and infrared radiation (IR).
UV radiation consists only 2% of solar radiation and it is not visible to human eye. It does not produce heat but it is responsible for the physical damage of fabrics, wooden furniture and paintings. You have the option to eliminate this radiation by choosing one of the glasses that comprise double glazing to be laminated. The PVB interlayer work as a filter and prevents the passing of ultraviolet radiation.
Visible radiation, that is, visible light, with a percentage of 47% is what gives lighting in a room. With the double glazing you have the capability to determine how much light passes through with high light transmission glasses for a lot of light and with low light transmission glasses for the opposite result.
Infrared radiation, also invisible to human eye, with the high percentage of 51% causes the feeling of heat. In a country like Cyprus, with almost nine months of sunlight, controlling infrared radiation constitutes a need and not an option. So, with a good double glazing composition you can restrict heat transmission by more than 60% (even 80%).

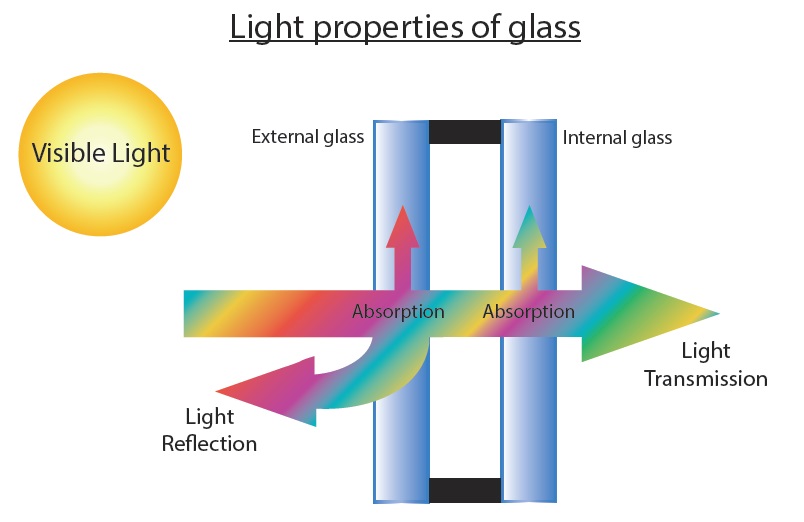
The specifications of a double glazing will help you decide if it is the proper one for the building to which will be applied. The four characteristics that you should pay more attention to are: Light Transmission, Light Reflection, Solar Factor and Thermal Conductance (U-value/Ug). In the certificate you will ask, you will notice the first two in the light properties of the double glazing and the rest in the energy properties.
Specifically, when visible radiation reaches the surface of the external glass, then the following division happens: some of the percentage passes through (Transmission), some is absorbed and the rest is reflected (Reflection). An accepted light transmission percentage for houses is 60% and bigger while for reflection is 25% and smaller. Smaller transmission percentage results in less lighting internally and bigger reflection percentage means the glass is reflective (mirror effect) which is more common in building and not houses.
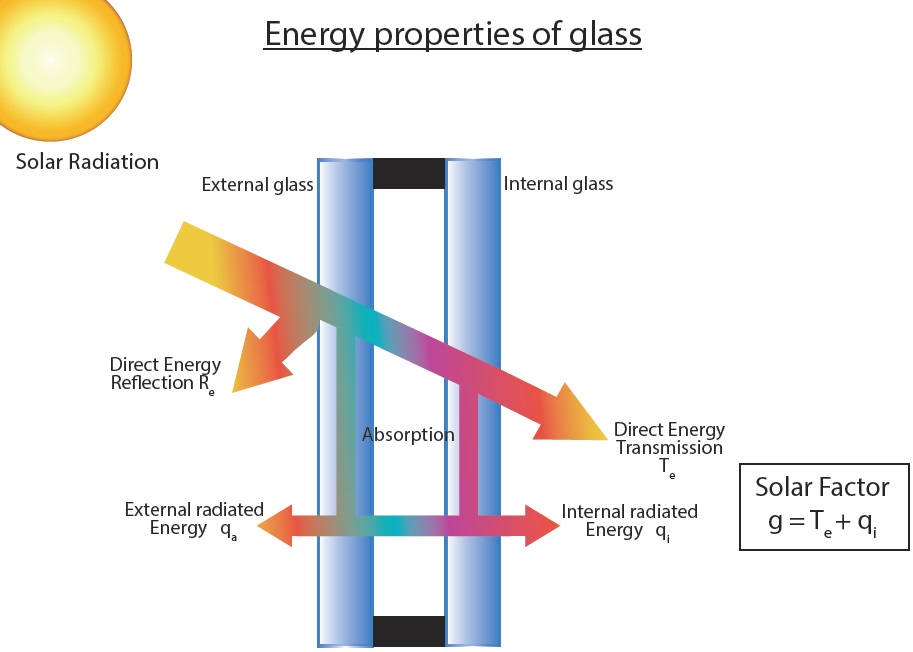
Parallel to visible radiation, the division of infrared radiation happens as well. The percentage that is directly transmitted (Te), plus the one indirectly transmitted (qi) by heating the external glass and then the internal, comprise the Solar Factor (g). This factor, is considered even more important than U-value because of the Cyprus’s hot weather. In the present, the most popular energy glasses have a solar factor of 40% and the tendency now is for a lot lower than that. This means that they prevent 60% of the heat that reaches the glass. It should be noted that this characteristic of the glass is not affected by its thickness.
As for the thermal conductance factor or U-value, is also very important since it directly affects the electricity consumption. By definition, U-value is equal to watts divided by the m2 of window frame and multiplied by the temperature difference inside and outside of the building (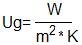 ). U-value is affected by the type of the glass (energy glass or not) and from the size of the gap and like solar factor, the lower the better. The gap that gives the maximum U-value that the glass can offer is 16mm. The example that follows will make U-value definition more understandable which we convert into watts and thus making obvious how it affects electricity consumption. The lower the U-value is, the lower the consumption.
). U-value is affected by the type of the glass (energy glass or not) and from the size of the gap and like solar factor, the lower the better. The gap that gives the maximum U-value that the glass can offer is 16mm. The example that follows will make U-value definition more understandable which we convert into watts and thus making obvious how it affects electricity consumption. The lower the U-value is, the lower the consumption.
E.g. we have a window with dimensions 100 x 100cm. Outside temperature 40°C and inside 25°C. → m2=1, K= 15
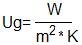 → W=Ug*m2*K
→ W=Ug*m2*K
| Ug* = 5.8 (Single glazing) | W = 5.8 * 1 * 15 = 87.0 |
| Ug* = 2.6 (Double glazing-not energy glasses) | W = 2.6 * 1 * 15 = 39.5 |
| Ug* = 1.6 (Double glazing with low-e coating) | W = 1.5 * 1 * 15 = 22.5 |
| Ug* = 1.0 (Double glazing with high performance coating) | W = 1.0 * 1 * 15 = 15.0 |
* U-value results from a double glazing with 16mm gap with argon
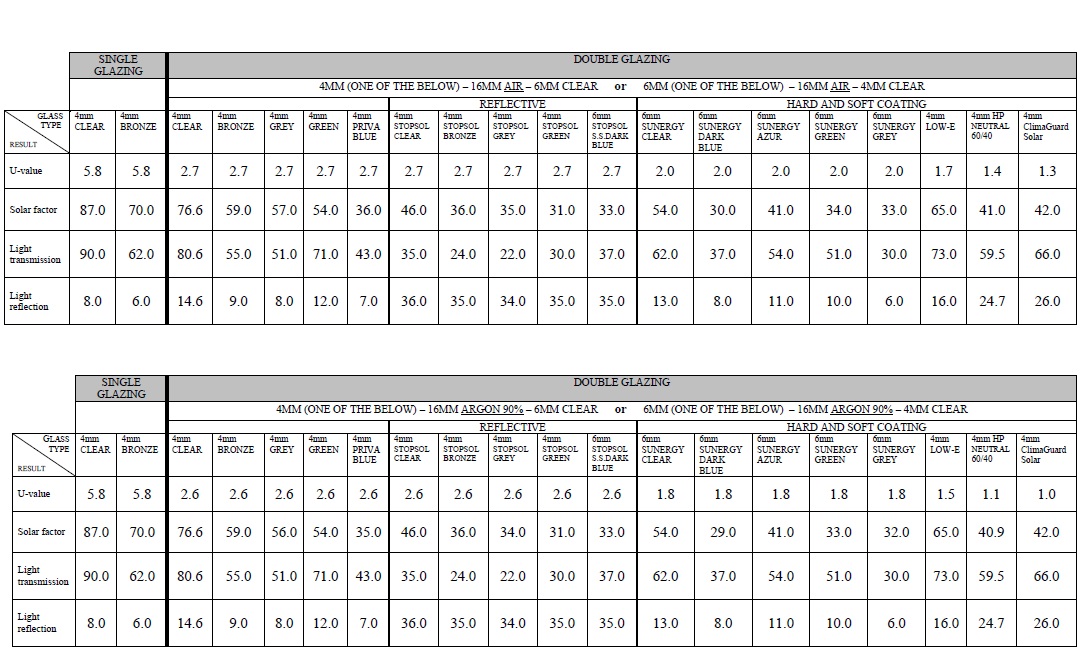
So, from the above results, compared to a simple double glazing, it is clear that with a high performance double glazing, you can achieve a reduction of the electricity consumption of your air-conditioning or heating of more than 62%! In the table below you will find various double glazing compositions and their performance in the four characteristics that were analysed previously.
Extra advices
• Double glazing with one or two energy glasses?
There is no reason to sacrifice money for two energy glasses when high performance energy glasses exist that cost less and offer more than two energy glasses together. You can contact us for more details.
• What is laminated glass and why should I incorporate it in the double glazing?
Laminated glass is a combination of one or more glass sheets, with one or more plastic interlayers (PVB) which in case of breakage holds the fragments together. So, you will choose laminated glass for the following reasons:
→ If you want to prevent the transmission of UV radiation that causes physical damage of furniture and fabrics
→ If you wish to have the increased sound insulation given by the PVB
→ Due to safety reasons in case of breakage and that is why we recommend this glass for large permanent opening and doors
• What should be the thickness of the two glasses?
It is recommended for sound insulation reasons, the two glasses to have at least 1mm difference from one another (e.g. 4mm + 5mm). As for U-value factor, the thickness will not play much difference in the glass’s performance. Lastly, the thickness choice will depend on the size of the window or door frame. Please contact us to give you the right combination.
• What is the maximum size that a double glazing can be produced?
The glass is imported in specific dimensions. So, before you decide how big your openings will be, please contact us to make sure the glass is available in that dimensions.
• Is it necessary to choose to have a thermal double glazing with a thermal alouminium profile?
Thermal double glazing and thermal profile is the best combination but it implies bigger budget as well. Definitely though, the existence of both should not be binding. The energy glass should absolutely be part of the double glazing as it will cover 80% of the surface of the window/door frame.
We hope we have been helpful in understanding the importance of double glazing for your house and that the choice of it should not be left in luck or based only on cost. We remain at your disposal for any clarifications, specifications or any other information you may need.
With respect,
Christothea Shikki-Lagou
Assistant Manager

